Publications
publications by categories in reversed chronological order. generated by jekyll-scholar.
2025
-
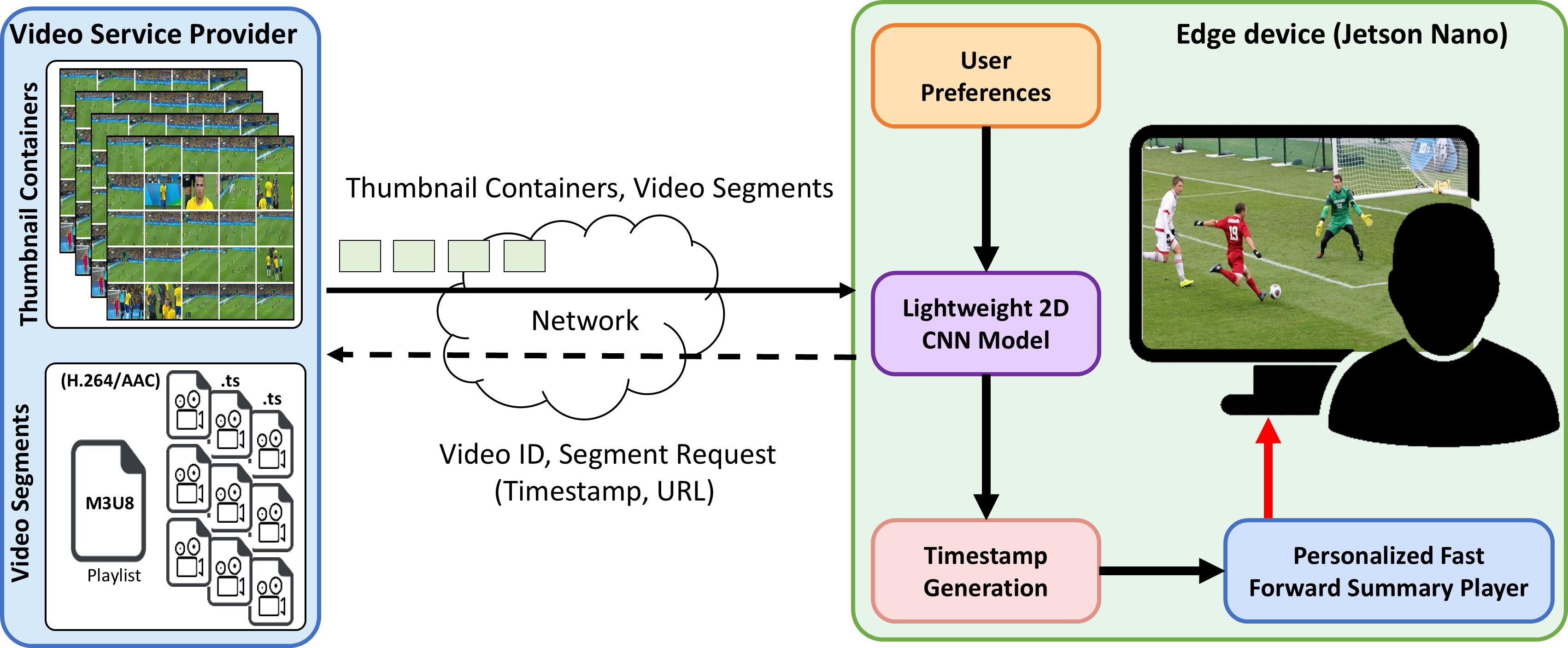 EdgeVidSum: Real-Time Personalized Video Summarization at the EdgeGhulam Mujtaba, and Eun-Seok RyuIn Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR)-Demo, 2025
EdgeVidSum: Real-Time Personalized Video Summarization at the EdgeGhulam Mujtaba, and Eun-Seok RyuIn Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR)-Demo, 2025EdgeVidSum is a lightweight framework designed to generate personalized summaries of long-form videos directly on edge devices. The proposed approach enables real-time video summarization while safeguarding user privacy through local data processing using innovative thumbnail-based techniques and efficient neural architectures. Our interactive demo highlights the system’s capability to create tailored video summaries for long-form videos like movies, sports events, and TV shows based on individual user preferences. The entire computations occur seamlessly on resource-constrained devices like Jetson Nano.
@inproceedings{CVPR_EdgeVidSum2025, title = {EdgeVidSum: Real-Time Personalized Video Summarization at the Edge}, author = {Mujtaba, Ghulam and Ryu, Eun-Seok}, booktitle = {Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR)-Demo}, year = {2025}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.48550/arXiv.2506.03171}, dimensions = {}, } -
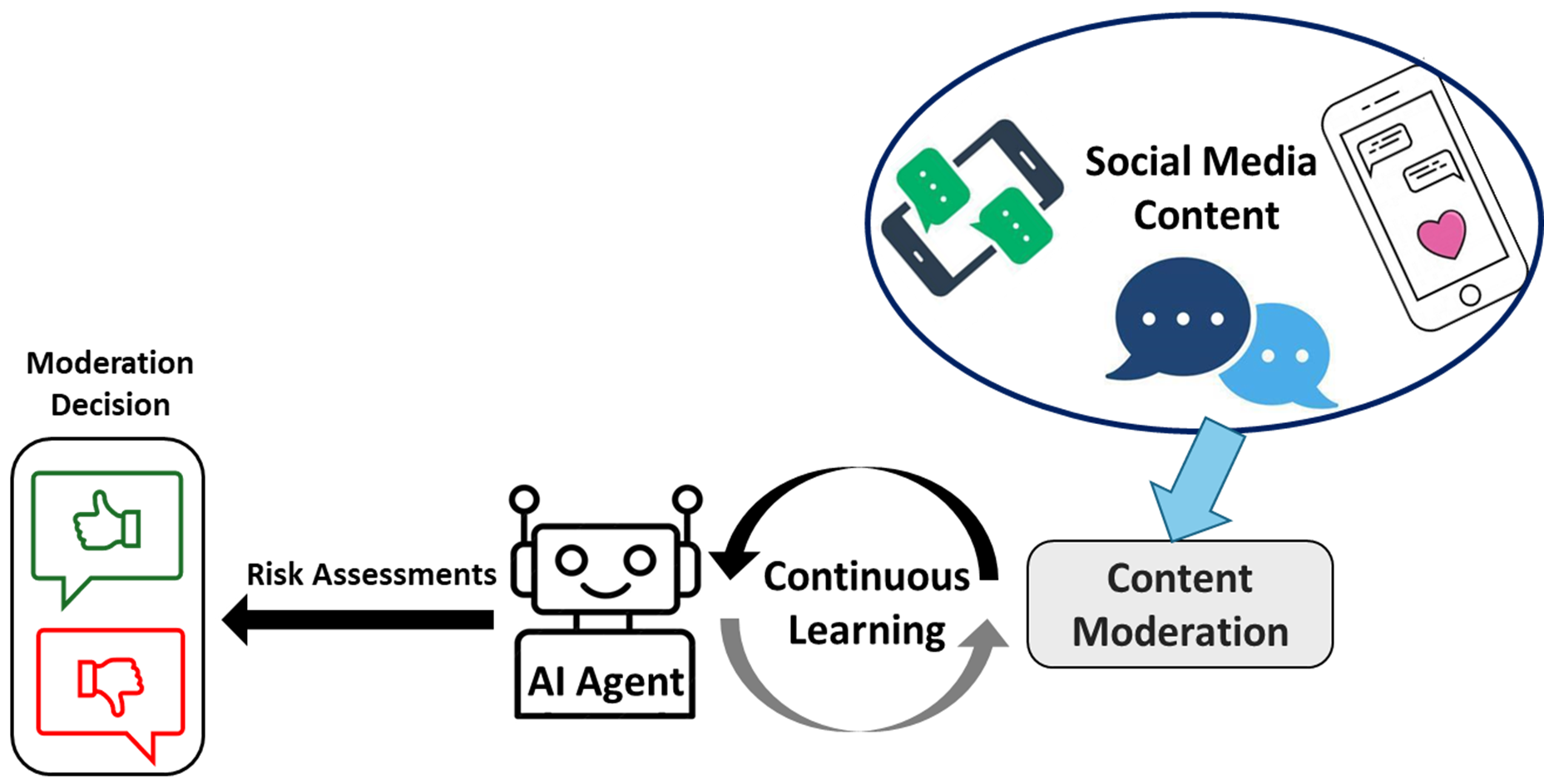 EdgeAIGuard: Agentic LLMs for Minor Protection in Digital SpacesGhulam Mujtaba, Sunder Ali Khowaja, and Kapal DevIEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2025
EdgeAIGuard: Agentic LLMs for Minor Protection in Digital SpacesGhulam Mujtaba, Sunder Ali Khowaja, and Kapal DevIEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2025Social media has become integral to minors’ daily lives and is used for various purposes, such as making friends, exploring shared interests, and engaging in educational activities. However, the increase in screen time has also led to heightened challenges, including cyberbullying, online grooming, and exploitations posed by malicious actors. Traditional content moderation techniques have proven ineffective against exploiters’ evolving tactics. To address these growing challenges, we propose the EdgeAIGuard content moderation approach that is designed to protect minors from online grooming and various forms of digital exploitation. The proposed method comprises a multi-agent architecture deployed strategically at the network edge to enable rapid detection with low latency and prevent harmful content targeting minors. The experimental results show the proposed method is significantly more effective than the existing approaches.
@article{edgeaiguard2025, title = {EdgeAIGuard: Agentic LLMs for Minor Protection in Digital Spaces}, author = {Mujtaba, Ghulam and Khowaja, Sunder Ali and Dev, Kapal}, journal = {IEEE Internet of Things Journal}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/JIOT.2025.3574961}, year = {2025}, dimensions = {false}, }
2024
-
 FISTNet: Fusion of style-path generative networks for facial style transferSunder Ali Khowaja, Lewis Nkenyereye, Ghulam Mujtaba, and 3 more authorsInformation Fusion, 2024
FISTNet: Fusion of style-path generative networks for facial style transferSunder Ali Khowaja, Lewis Nkenyereye, Ghulam Mujtaba, and 3 more authorsInformation Fusion, 2024With the surge in emerging technologies such as Metaverse, spatial computing, and generative AI, the application of facial style transfer has gained much interest from researchers and startups enthusiasts alike. StyleGAN methods have paved the way for transfer-learning strategies that could reduce the dependency on the vast data available for the training process. However, StyleGAN methods tend to need to be more balanced, resulting in the introduction of artifacts in the facial images. Studies such as DualStyleGAN proposed multipath networks but required the networks to be trained for a specific style rather than simultaneously generating a fusion of facial styles. In this paper, we propose a Fusion of STyles (FIST) network for facial images that leverages pretrained multipath style transfer networks to eliminate the problem associated with the lack of enormous data volume in the training phase and the fusion of multiple styles at the output. We leverage pretrained styleGAN networks with an external style pass that uses a residual modulation block instead of a transform coding block. The method also preserves facial structure, identity, and details via the gated mapping unit introduced in this study. The aforementioned components enable us to train the network with minimal data while generating high-quality stylized images, opening up new possibilities for facial style transfer in emerging technologies. Our training process adapts curriculum learning strategy to perform efficient, flexible style, and model fusion in the generative space. We perform extensive experiments to show the superiority of the proposed FISTNet compared to existing state-of-the-art methods.
@article{KHOWAJA2024102572, title = {FISTNet: Fusion of style-path generative networks for facial style transfer}, author = {Ali Khowaja, Sunder and Nkenyereye, Lewis and Mujtaba, Ghulam and Lee, Ik Hyun and Fortino, Giancarlo and Dev, Kapal}, journal = {Information Fusion}, volume = {}, pages = {}, year = {2024}, publisher = {Elsevier}, doi = {10.1016/j.inffus.2024.102572}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 Personalized semantic fast-forward videos for next generation streaming platformsGhulam Mujtaba, Eun-Seok Ryu, and Reda HarbUSA Patent, 2024
Personalized semantic fast-forward videos for next generation streaming platformsGhulam Mujtaba, Eun-Seok Ryu, and Reda HarbUSA Patent, 2024Systems and methods are provided herein for generating a summary for a piece of content using a thumbnail container. This may be accomplished by a system receiving a thumbnail container related to a piece of content. The system may also receive user information, a device characteristic, and/or content information related to the piece of content and use the received data to select a machine learning model. The selected machine learning model can identify one or more thumbnails of the thumbnail container as a thumbnail of interest to a user. The system can then generate a summary of the piece of content based on the thumbnail identified by the machine learning model and display the generated summary for the user.
@article{mujtaba2024ff, title = {Personalized semantic fast-forward videos for next generation streaming platforms}, author = {Mujtaba, Ghulam and Ryu, Eun-Seok and Harb, Reda}, journal = {USA Patent}, volume = {}, pages = {}, year = {2024}, publisher = {USA Patent}, }
2023
-
 FRC-GIF: Frame Ranking-based Personalized Artistic Media Generation Method for Resource Constrained DevicesGhulam Mujtaba, Sunder Ali Khowaja, Muhammad Aslam Jarwar, and 2 more authorsIEEE Transactions on Big Data, 2023
FRC-GIF: Frame Ranking-based Personalized Artistic Media Generation Method for Resource Constrained DevicesGhulam Mujtaba, Sunder Ali Khowaja, Muhammad Aslam Jarwar, and 2 more authorsIEEE Transactions on Big Data, 2023Generating video highlights in the form of animated graphics interchange formats (GIFs) has significantly simplified the process of video browsing. Animated GIFs have paved the way for applications concerning streaming platforms and emerging technologies. Existing studies have led to large computational complexity without considering user personalization. This paper proposes lightweight method to attract users and increase views of videos through personalized artistic media, i.e., static thumbnails and animated GIF generation. The proposed method analyzes lightweight thumbnail containers (LTC) using the computational resources of the client device to recognize personalized events from feature-length sports videos. Next, the thumbnails are then ranked through the frame rank pooling method for their selection. Subsequently, the proposed method processes small video segments rather than considering the whole video for generating artistic media. This makes our approach more computationally efficient compared to existing methods that use the entire video data; thus, the proposed method complies with sustainable development goals. Furthermore, the proposed method retrieves and uses thumbnail containers and video segments, which reduces the required transmission bandwidth as well as the amount of locally stored data. Experiments reveal that the computational complexity of our method is 3.73 times lower than that of the state-of-the-art method.
@article{mujtaba2023frc, title = {FRC-GIF: Frame Ranking-based Personalized Artistic Media Generation Method for Resource Constrained Devices}, author = {Mujtaba, Ghulam and Ali Khowaja, Sunder and Aslam Jarwar, Muhammad and Choi, Jaehyuk and Ryu, Eun-Seok}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Big Data}, volume = {}, pages = {1-14}, year = {2023}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/TBDATA.2023.3338012}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 Education 5.0: requirements, enabling technologies, and future directionsShabir Ahmad, Sabina Umirzakova, Ghulam Mujtaba, and 2 more authorsarXiv preprint arXiv:2307.15846, 2023
Education 5.0: requirements, enabling technologies, and future directionsShabir Ahmad, Sabina Umirzakova, Ghulam Mujtaba, and 2 more authorsarXiv preprint arXiv:2307.15846, 2023We are currently in a post-pandemic era in which life has shifted to a digital world. This has affected many aspects of life, including education and learning. Education 5.0 refers to the fifth industrial revolution in education by leveraging digital technologies to eliminate barriers to learning, enhance learning methods, and promote overall well-being. The concept of Education 5.0 represents a new paradigm in the field of education, one that is focused on creating a learner-centric environment that leverages the latest technologies and teaching methods. This paper explores the key requirements of Education 5.0 and the enabling technologies that make it possible, including artificial intelligence, blockchain, and virtual and augmented reality. We analyze the potential impact of these technologies on the future of education, including their ability to improve personalization, increase engagement, and provide greater access to education. Additionally, we examine the challenges and ethical considerations associated with Education 5.0 and propose strategies for addressing these issues. Finally, we offer insights into future directions for the development of Education 5.0, including the need for ongoing research, collaboration, and innovation in the field. Overall, this paper provides a comprehensive overview of Education 5.0, its requirements, enabling technologies, and future directions, and highlights the potential of this new paradigm to transform education and improve learning outcomes for students.
@article{ahmad2023education, title = {Education 5.0: requirements, enabling technologies, and future directions}, author = {Ahmad, Shabir and Umirzakova, Sabina and Mujtaba, Ghulam and Amin, Muhammad Sadiq and Whangbo, Taegkeun}, journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.15846}, doi = {10.48550/arXiv.2307.15846}, year = {2023}, dimensions = {true}, }
2022
-
 LTC-SUM: Lightweight Client-driven Personalized Video Summarization Framework Using 2D CNNGhulam Mujtaba, Adeel Malik, and Eun-Seok RyuIEEE Access, 2022
LTC-SUM: Lightweight Client-driven Personalized Video Summarization Framework Using 2D CNNGhulam Mujtaba, Adeel Malik, and Eun-Seok RyuIEEE Access, 2022This paper proposes a novel lightweight thumbnail container-based summarization (LTC-SUM) framework for full feature-length videos. This framework generates a personalized keyshot summary for concurrent users by using the computational resource of the end-user device. State-of-the-art methods that acquire and process entire video data to generate video summaries are highly computationally intensive. In this regard, the proposed LTC-SUM method uses lightweight thumbnails to handle the complex process of detecting events. This significantly reduces computational complexity and improves communication and storage efficiency by resolving computational and privacy bottlenecks in resource-constrained end-user devices. These improvements were achieved by designing a lightweight 2D CNN model to extract features from thumbnails, which helped select and retrieve only a handful of specific segments. Extensive quantitative experiments on a set of full 18 feature-length videos (approximately 32.9 h in duration) showed that the proposed method is significantly computationally efficient than state-of-the-art methods on the same end-user device configurations. Joint qualitative assessments of the results of 56 participants showed that participants gave higher ratings to the summaries generated using the proposed method. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first attempt in designing a fully client-driven personalized keyshot video summarization framework using thumbnail containers for feature-length videos.
@article{mujtaba2022ltc, title = {LTC-SUM: Lightweight Client-driven Personalized Video Summarization Framework Using 2D CNN}, author = {Mujtaba, Ghulam and Malik, Adeel and Ryu, Eun-Seok}, journal = {IEEE Access}, volume = {10}, pages = {103041--103055}, year = {2022}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3209275}, dimensions = {true}, } -
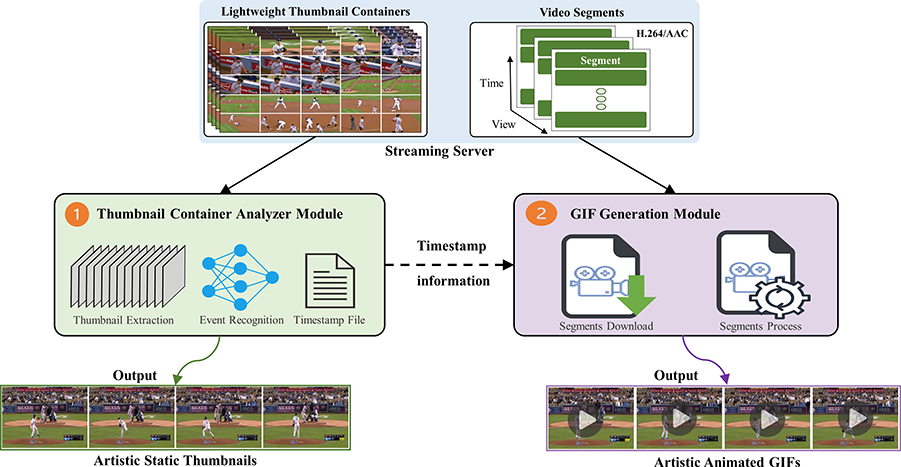 Client-driven lightweight method to generate artistic media for feature-length sports videosGhulam Mujtaba, Jaehyuk Choi, and Eun-Seok RyuIn SIGMAP: 19th International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications, 2022
Client-driven lightweight method to generate artistic media for feature-length sports videosGhulam Mujtaba, Jaehyuk Choi, and Eun-Seok RyuIn SIGMAP: 19th International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications, 2022This paper proposes a lightweight methodology to attract users and increase views of videos through personalized artistic media i.e., static thumbnails and animated Graphics Interchange Format (GIF) images. The proposed method analyzes lightweight thumbnail containers (LTC) using computational resources of the client device to recognize personalized events from feature-length sports videos. In addition, instead of processing the entire video, small video segments are used in order to generate artistic media. This makes our approach more computationally efficient compared to existing methods that use the entire video data. Further, the proposed method retrieves and uses thumbnail containers and video segments, which reduces the required transmission bandwidth as well as the amount of locally stored data that are used during artistic media generation. After conducting experiments on the NVIDIA Jetson TX2, the computational complexity of our method was 3:78 times lower than that of the state-of-the-art method. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first technique that uses LTC to generate artistic media while providing lightweight and high-performance services on resource-constrained devices.
@inproceedings{mujtaba2022client, title = {Client-driven lightweight method to generate artistic media for feature-length sports videos}, author = {Mujtaba, Ghulam and Choi, Jaehyuk and Ryu, Eun-Seok}, booktitle = {SIGMAP: 19th International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications}, pages = {102--111}, year = {2022}, publisher = {SCITEPRESS}, doi = {10.5220/0011335300003289}, dimensions = {true}, }
2021
-
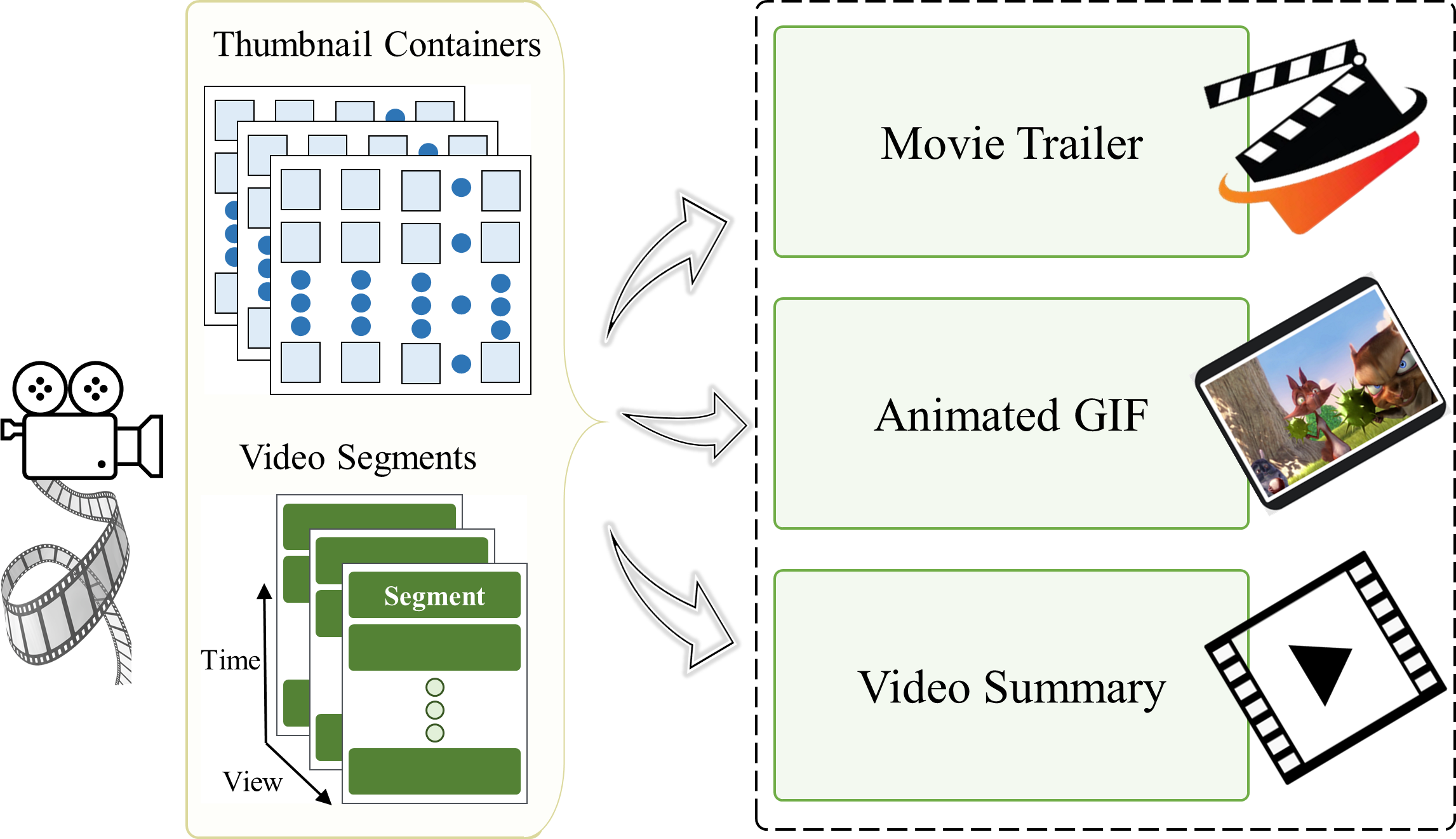 Lightweight client-driven personalized multimedia framework for next generation streaming platformsGhulam MujtabaPhD Dissertation, 2021
Lightweight client-driven personalized multimedia framework for next generation streaming platformsGhulam MujtabaPhD Dissertation, 2021This dissertation presents a client-driven personalized multimedia content generation framework for streaming platforms. The proposed framework can generate several personalized multimedia contents for feature-length videos on the end-user devices, such as movie trailers, animated GIFs, and video summaries simultaneously. The state-of-the-art methods that acquire and process entire video data to generate personalized multimedia are highly computationally intensive. In this regard, the proposed framework uses lightweight thumbnail containers to handle the complex process of detecting events parallelly resolving computational and privacy bottlenecks on the resource-constrained end-user devices. This significantly reduces computational complexity and improves communication (between server and client) and storage efficiency. These improvements are achieved by extracting features from thumbnails, which helped select and retrieve just a handful of specific segments. In this context, the 2D CNN model is designed that can extract features from thumbnails. The framework is designed to manage a wide range of end-user hardware platforms with heterogeneous computing, networks, and storage capabilities.
@article{mujtaba2021lightweight, title = {Lightweight client-driven personalized multimedia framework for next generation streaming platforms}, author = {Mujtaba, Ghulam}, journal = {PhD Dissertation}, year = {2021}, publisher = {Gachon University, Seongnam, Korea}, } -
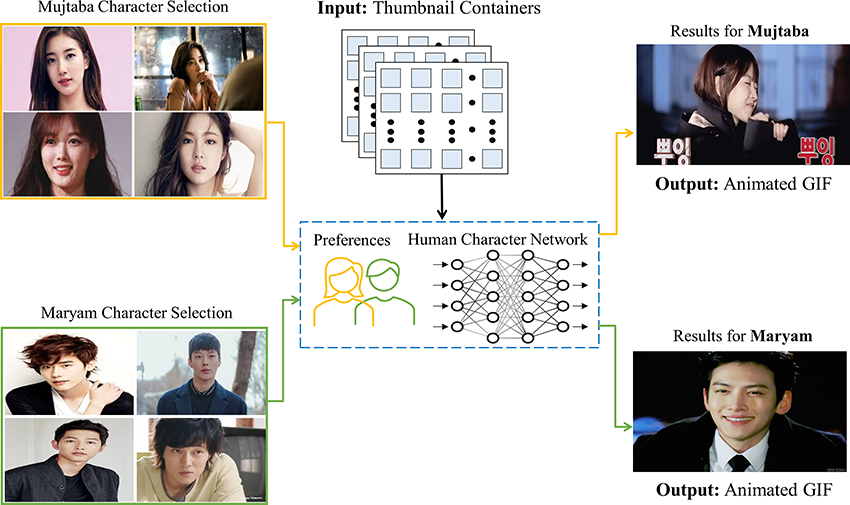 Human character-oriented animated gif generation frameworkGhulam Mujtaba, and Eun-Seok RyuIn MAJICC: Mohammad Ali Jinnah University International Conference on Computing, 2021
Human character-oriented animated gif generation frameworkGhulam Mujtaba, and Eun-Seok RyuIn MAJICC: Mohammad Ali Jinnah University International Conference on Computing, 2021Click-through rate (CTR) is a critical metric to boost the popularity of newly published videos on streaming platforms. Humans and human-like characters play a significant role in GIF selection and improving the CTR of the video. This paper proposes a new lightweight method to generate human character-oriented animated GIFs using the end-user device’s computational capabilities. Instead of analyzing full video, the proposed method analyzes the lightweight thumbnail containers to decrease computational complexity in the GIF generation process. Moreover, it uses the segment to generate the GIF and reduced valuable network bandwidth and storage demands in the user end. A feed-forward 2D deep neural network trained on the CelebA dataset is designed to detect humans or humanlike characters and their gender. Experimental evaluations and results performed in 10 full videos showed that the proposed method is 2.34 times more computationally efficient than the SoA approach. The proposed method is designed to support end-user devices with different computational capabilities.
@inproceedings{mujtaba2021human, title = {Human character-oriented animated gif generation framework}, author = {Mujtaba, Ghulam and Ryu, Eun-Seok}, booktitle = {MAJICC: Mohammad Ali Jinnah University International Conference on Computing}, pages = {1--6}, year = {2021}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/MAJICC53071.2021.9526249}, dimensions = {true}, } -
 Client-driven animated gif generation framework using an acoustic featureGhulam Mujtaba, Sangsoon Lee, Jaehyoun Kim, and 1 more authorMultimedia Tools and Applications, 2021
Client-driven animated gif generation framework using an acoustic featureGhulam Mujtaba, Sangsoon Lee, Jaehyoun Kim, and 1 more authorMultimedia Tools and Applications, 2021This paper proposes a novel, lightweight method to generate animated graphical interchange format images (GIFs) using the computational resources of a client device. The method analyzes an acoustic feature from the climax section of an audio file to estimate the timestamp corresponding to the maximum pitch. Further, it processes a small video segment to generate the GIF instead of processing the entire video. This makes the proposed method computationally efficient, unlike baseline approaches that use entire videos to create GIFs. The proposed method retrieves and uses the audio file and video segment so that communication and storage efficiencies are improved in the GIF generation process. Experiments on a set of 16 videos show that the proposed approach is 3.76 times more computationally efficient than a baseline method on an Nvidia Jetson TX2. Additionally, in a qualitative evaluation, the GIFs generated using the proposed method received higher overall ratings compared to those generated by the baseline method. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first technique that uses an acoustic feature in the GIF generation process.
@article{mujtaba2021client, title = {Client-driven animated gif generation framework using an acoustic feature}, author = {Mujtaba, Ghulam and Lee, Sangsoon and Kim, Jaehyoun and Ryu, Eun-Seok}, journal = {Multimedia Tools and Applications}, pages = {1--18}, year = {2021}, publisher = {Springer}, doi = {10.1007/s11042-020-10236-6}, dimensions = {true}, }
2020
-
 Client-driven personalized trailer framework using thumbnail containersGhulam Mujtaba, and Eun-Seok RyuIEEE Access, 2020
Client-driven personalized trailer framework using thumbnail containersGhulam Mujtaba, and Eun-Seok RyuIEEE Access, 2020Movie trailers are prepared using a one-size-fits-all framework. These days, however, streaming platforms seek to overcome this problem and provide personalized trailers via the investigation of centralized server-side solutions. This can be achieved by analyzing personal user data, and can lead to two major issues: privacy violation and enormous demand in computational resources. This paper proposes an innovative, low-power, client-driven method to facilitate the personalized trailer generation process. It tackles the complex process of detecting personalized actions in real-time from lightweight thumbnail containers. The HTTP live streaming (HLS) server and client are locally configured to validate the proposed method. The system is designed to support a wide range of client hardware with different computational capabilities and has the flexibility to adapt to network conditions. To test the effectiveness of this method, twenty-five broadcast movies, specifically in the western and sports genres, are evaluated. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first-ever client-driven framework that uses thumbnail containers as input to facilitate the trailer generation process.
@article{mujtaba2020client, title = {Client-driven personalized trailer framework using thumbnail containers}, author = {Mujtaba, Ghulam and Ryu, Eun-Seok}, journal = {IEEE Access}, volume = {8}, pages = {60417--60427}, year = {2020}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2982992}, dimensions = {true}, }
2019
-
 Energy efficient data encryption techniques in smartphonesGhulam Mujtaba, Muhammad Tahir, and Muhammad Hanif SoomroWireless Personal Communications, 2019
Energy efficient data encryption techniques in smartphonesGhulam Mujtaba, Muhammad Tahir, and Muhammad Hanif SoomroWireless Personal Communications, 2019Mobile devices have been increased exceptionally in recent years, consequently data generation has also been raised exceptionally. Most of the data generated by mobile devices is transferred to servers for processing and storage. Managing security of mobile data is a necessary feature of every network and mostly encryption is used to avoid security breaches. The major challenge is that, mobile devices are very small with shortage of resources, on the other hand encryption of data requires extra energy. It is necessary to minimize energy requirements for encryption of data. For this experimental research, an android based application is developed, which optimize energy requirements for both single and double encryption techniques. AES and Blowfish encryption algorithms are used with different files sizes to test the energy requirements for single encryption, it is also examined that energy consumed by Blowfish is 119.311% more than AES. For double encryption methods, AES–Blowfish, Blowfish–AES and XTS–AES combinations of algorithms are used and energy usage is gathered. In double encryption XTS–AES consumed 13.26% less power consumption as compared to AES–Blowfish and 44.97% less then Blowfish–AES combination methods. Results of experiments revealed that AES is more energy efficient for single encryption and for double encryption XTS AES combination requires less energy.
@article{mujtaba2019energy, title = {Energy efficient data encryption techniques in smartphones}, author = {Mujtaba, Ghulam and Tahir, Muhammad and Soomro, Muhammad Hanif}, journal = {Wireless Personal Communications}, volume = {106}, number = {4}, pages = {2023--2035}, year = {2019}, publisher = {Springer}, doi = {10.1007/s11277-018-5920-1}, dimensions = {true}, }
